Welding is a critical process in manufacturing, but choosing the right welding method directly impacts product quality, efficiency, and production cost. As industries evolve, laser welding has emerged as a modern alternative to traditional welding methods such as arc welding, MIG welding, and TIG welding.
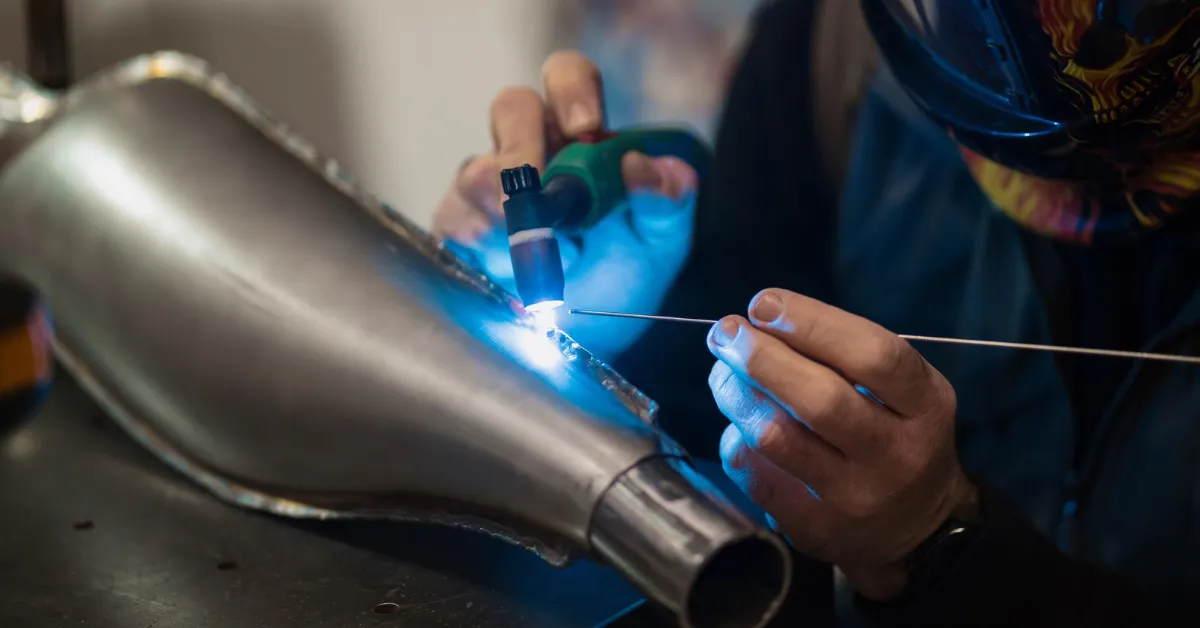
Traditional welding techniques rely on high heat and filler materials to join components. While these methods are widely used, they often result in larger heat-affected zones, distortion, spatter, and post-weld finishing requirements. This can slow down production and affect dimensional accuracy.
Laser welding, on the other hand, uses a highly focused laser beam to create precise and clean welds. The controlled heat input minimizes material deformation and produces strong, narrow, and visually clean weld joints. This makes laser welding ideal for thin materials and complex components.
Looking to improve weld quality, speed, and efficiency in your production line?
Connect with Unique Laser today to explore advanced laser welding machines designed for precision-driven industrial applications.
Another major advantage of laser welding is speed and automation. Laser welding systems integrate easily with automated production lines, enabling faster cycle times and consistent weld quality across large volumes.
Industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, battery manufacturing, and precision engineering increasingly prefer laser welding due to its accuracy, repeatability, and reduced rework.
While traditional welding still has its place in heavy fabrication and outdoor applications, laser welding offers superior precision, efficiency, and long-term cost benefits, making it the preferred choice for modern manufacturing environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Laser welding uses a focused laser beam for precise heat control, while traditional welding relies on broader heat sources and filler materials, leading to more distortion.
Yes, laser welding produces deep penetration and uniform welds, often resulting in stronger and more reliable joints compared to traditional welding.
Absolutely. Laser welding is ideal for thin and delicate materials due to its low heat input and precise control.
Yes. Laser welding is highly suitable for high-volume and automated production lines due to its speed, consistency, and repeatability.
Traditional welding is suitable for heavy structures, outdoor applications, and projects where ultra-high precision is not required.
Conclusion
Both laser welding and traditional welding have their applications, but laser welding clearly stands out for modern manufacturing needs. With higher precision, reduced distortion, faster production cycles, and improved consistency, laser welding helps manufacturers achieve superior quality while lowering operational costs.
As industries continue to demand tighter tolerances and higher efficiency, laser welding has become a strategic investment rather than just a technological upgrade.